9 Often-Missed ADHD Signs: From Self-Discovery to Professional Diagnosis
- Redwood Psychology Team
- Feb 13
- 13 min read
Updated: Mar 13

Image Source: Unsplash
Adult ADHD diagnoses are growing four times faster than childhood diagnoses. Many people think ADHD only affects children, yet this condition touches the lives of up to 5% of adults worldwide.
ADHD symptoms substantially affect an adult's personal relationships, work performance, and emotional well-being. Adults with ADHD often face additional challenges. More than half of them struggle with other behavioural health issues like depression or anxiety. These challenges lead to a pile of unfinished tasks that become overwhelming.
In this article, we highlight nine frequently overlooked signs of ADHD. These signs often go unnoticed in typical discussions about ADHD. These insights can guide you to decide whether you want to learn more about yourself or plan to seek professional help.

Image Source: Medium
"Life is an adventure or nothing at all. And adventures will make you late for dinner." — Anonymous, ADHD individual
Time blindness is one of the toughest yet rarely discussed symptoms of ADHD. A recent survey of 1,859 adults with ADHD revealed that and important tasks. The data also shows 31% of the surveyed adults find it hard to estimate how long tasks will take. 57% of adults with ADHD struggle with procrastination.
Understanding Time Blindness in ADHD
Time blindness shows up as the inability to sense time passing or estimate task duration accurately. The ADHD brain processes time differently - it's not about ignoring time on purpose. Studies show that 80% of adults with ADHD face challenges with time management and organization . The ADHD brain works in two modes: "now" and "not now," which makes planning ahead really tough.
Impact on Professional Life
Time blindness can seriously affect your work life. Survey data shows that 42% of adults with ADHD have trouble resisting distractions, so their work performance suffers. Time blindness often results in:
· Chronic lateness to meetings
· Rushed last-minute work
· Missed project deadlines
· Trouble keeping steady productivity
Digital Tools for Time Management
Digital solutions have become valuable allies to manage time blindness. We found that 37% of people say time management tools help them handle productivity issues. Setting multiple alarms with 5-minute "pre-timers" prevents hyperfocus, while calendar systems with built-in reminders work well too.
Body doubling is a practice where a person with ADHD does potentially frustrating or boring tasks in the presence of someone else. Body-doubling, both virtually and in-person, helps maintain accountability effectively. Visual timers and time-tracking apps create a real sense of time passing. Music playlists of specific lengths can mark time naturally throughout daily tasks for better results.

Image Source: Simply Psychology
"Sometimes the working memory impairments of ADHD allow a momentary emotion to become too strong; the person is flooded with one emotion and unable to attend to other emotions, facts, and memories relevant to that immediate situation." — Thomas E. Brown, Clinical psychologist and ADHD expert
ADHD patients often struggle with emotional dysregulation. Research shows 30% - 70% of adults and 25% - 45% of children find it hard to manage their emotions.
ADHD and Emotional Dysregulation
Brain differences create a strong link between ADHD and emotional challenges. People with ADHD have an overactive amygdala and an underactive prefrontal cortex. This combination sets up the perfect storm for intense emotions. Their brain structure explains why they feel emotions more deeply and find it hard to control their responses.
Studies show emotional dysregulation appears through several signs:
· Reactions that don't match the situation
· Trouble calming down even when you know you're overreacting
· Getting frustrated easily
· Emotional outbursts that come out of nowhere
· Feelings that don't go away
Managing Emotional Responses
People with ADHD respond well to mindfulness-based techniques that help control emotions. The process works in three steps: you observe your emotions, describe them, and act with awareness. Physical exercise and music also help channel emotional energy in better ways.
The secret lies in building practical coping strategies. Putting a name to your emotions can make them less intense. Writing down emotional triggers and responses in a journal creates space between feelings and reactions. This space lets you respond more thoughtfully.
When to Seek Professional Help for ADHD Diagnosis & Therapy
You should consider getting professional help if emotional dysregulation gets in the way of your daily life. Studies show up to 73% of people with ADHD struggle with emotional dysregulation. Cognitive behavioural therapy and dialectical behavior therapy work well to improve emotional control.
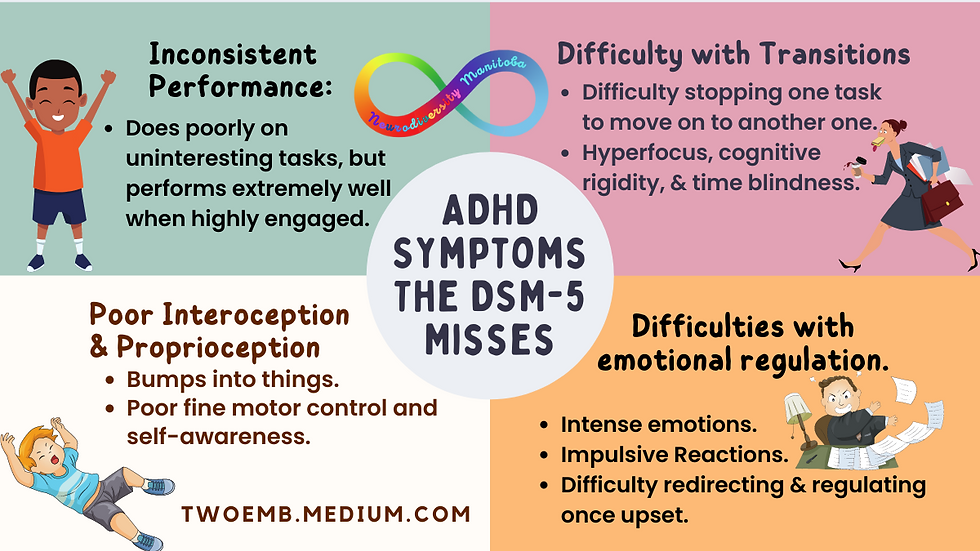
Image Source: Medium
People commonly misunderstand ADHD. The condition doesn't mean a lack of attention but rather inconsistent attention that activates under specific circumstances. This paradoxical nature becomes clear when we observe hyperfocus, where people experience intense concentration lasting for hours.
The Paradox of ADHD Attention
The ADHD nervous system works on interest rather than importance when controlling attention. Someone might struggle with simple tasks yet show remarkable focus on activities they enjoy. Studies show that hyperfocus happens when activities provide instant feedback or spark genuine interest.
Recognising Hyperfocus Patterns
You can spot hyperfocus through several distinct signs:
· Losing track of time completely
· Becoming oblivious to surroundings
· Difficulty transitioning to other tasks
· Postponing essential needs like eating or drinking
Activities like video games or social media often trigger hyperfocus states. This intense concentration can last hours without any awareness of time passing.
Balancing Interests with Responsibilities
Hyperfocus works as a double-edged sword. It enables exceptional productivity on interesting tasks, but it can lead to missed deadlines and strained relationships. On the other hand, many scientists, writers, and artists with ADHD channel this intense focus into successful careers.
External structure helps manage hyperfocus effectively. Timers, calendar systems, and accountability partnerships maintain balance. The goal isn't to eliminate hyperfocus but to realize its potential while preventing negative effects on daily responsibilities.
This paradoxical attention pattern plays a vital role in accurate ADHD diagnosis and treatment. Research shows that stimulant medications help maintain focus once engaged but don't help with starting tasks. Developing tailored strategies to direct attention becomes essential to manage ADHD symptoms effectively.
People with ADHD face unique challenges in making decisions. Research shows that directly affect how they make choices executive function difficulties.
Understanding ADHD Decision-Making
The ADHD brain works differently when making decisions. This happens because executive dysfunction affects planning, organization, and self-regulation. People with ADHD excel at making quick "hot decisions" in urgent situations. Yet they find it hard to handle "cold decisions" that need careful analysis. Research points to an as the reason. This part of the brain affects its feedback system for decision-making under-active anterior cingulate cortex.
Common Triggers
Decision paralysis in ADHD shows up through several key factors:
· Cognitive overload from multiple options
· Information processing challenges
· Emotionally overwhelmed during choice evaluation
· Past experiences creating decision anxiety
The paralysis gets worse with time pressure or complex choices. Research shows ADHD brains have trouble filtering out irrelevant information. This makes even small decisions feel overwhelming and can lead to decreased motivation and higher impulsivity.
Coping Strategies
Evidence-based strategies can help manage decision paralysis. Setting specific time limits for different types of decisions works well. The process can go on forever without these limits. Research backs using templates and routines for common decisions. This helps reduce mental load.
Breaking down decisions into smaller parts prevents feeling overwhelmed. Studies show that standard processes for regular choices help reduce decision fatigue. This includes using pre-made shopping lists or morning routines. Taking regular breaks during decision-making helps reset your mind and improves the quality of choices.
Writing through the process helps organise thoughts for big decisions. Limiting options to two or three prevents analysis paralysis, unless you need extensive research. Taking regular rest periods helps keep your mental energy up and this works for decisions of any size.
Social interactions take extensive mental energy if you have ADHD. Research shows that face-to-face communication needs you to process words, body language, and social cues simultaneously.
ADHD Social Processing Challenges
The ADHD brain processes social interactions differently because it struggles to filter irrelevant information. Research shows more than 50% of children with ADHD face peer rejection, and these challenges continue into adulthood. Face-to-face communication becomes especially demanding as it needs multiple cognitive tasks: listening attentively, analysing body language, maintaining appropriate eye contact, and masking symptoms.
Signs of Social Exhaustion
Social exhaustion shows through distinct physical and mental indicators:
· Cognitive fatigue and difficulty focusing
· Increased irritability or moodiness
· Physical symptoms like headaches or dizziness
· Withdrawal from social interactions
· Anxiety about upcoming social events
Studies show most people start experiencing social fatigue after 2-3 hours of interaction. But if you have ADHD, this exhaustion hits much sooner due to the extra cognitive demands of processing social information.
Creating Boundaries
Setting effective boundaries is vital to manage social energy. Research shows many people with ADHD struggle with boundary setting due to people-pleasing tendencies and guilt over past experiences. Of course, the challenge lies in balancing social connections with personal well-being.
Practical boundary-setting strategies include scheduling "reboot days" - time set aside without social interactions. Understanding that saying "no" is a form of self-care helps maintain energy levels. Studies show that building a supportive network that understands ADHD-related challenges helps maintain boundaries.
Proper boundary setting affects more than just social interactions. Research shows that clear limits prevent burnout, improve relationship quality, and boost overall well-being. Only when we are willing to spot early signs of social exhaustion and set appropriate boundaries can people with ADHD better manage their social energy while keeping meaningful connections.

Image Source: Inflow
People with ADHD often struggle with perfectionism as their main cognitive distortion. This creates a complex dynamic between setting high standards and getting things done. Many develop this perfectionist mindset to make up for past mistakes or feelings of not being good enough.
The ADHD-Perfectionism Connection
Research shows two main types of perfectionism in ADHD: front-end and back-end perfectionism. Front-end perfectionism shows up as strict rules people set before they start work. This affects how they begin tasks. Back-end perfectionism involves very high standards for quality and details, which makes it hard to finish tasks.
Common perfectionist traits in ADHD include:
· Setting unrealistic performance standards
· Too much self-criticism and comparing oneself to others
· Fear of mistakes or criticism
· All-or-nothing thinking patterns
· Problems with delegating tasks
People often use perfectionism as a shield to protect themselves from rejection. This protective strategy can backfire and lead to more stress and lower productivity.
Breaking the Avoidance Cycle
To break free from perfectionism-driven task avoidance, you need to understand why it happens. ADHD brains have lower dopamine levels. This makes it hard to work on tasks that seem boring or too big.
The perfectionism-avoidance cycle might feel better right now but adds more stress later. Studies show that the best way to deal with this is to challenge negative thoughts one step at a time and focus on realistic outcomes. Breaking tasks into smaller, achievable goals helps reduce unclear expectations that feed perfectionist tendencies.
Perfectionism isn't always bad. The key is to make use of its good parts while reducing how it interferes with daily life. This balanced approach, combined with good ADHD management strategies, helps create lasting progress in handling both perfectionism and task avoidance.

Image Source: ADDitude
Sensory processing challenges affect up to 60% of people with ADHD. These challenges create a complex relationship between environmental stimuli and daily functioning. Studies show that the ADHD brain processes sensory information differently and struggles to filter out unnecessary input.
Common Sensory Triggers
Research shows distinct patterns where people are either over-responsive or under-responsive to sensory input. Here are the most common triggers:
· Visual stimuli: Fluorescent lights and visual clutter
· Auditory input: Background conversations and repetitive sounds
· Tactile sensations: Clothing tags and certain fabric textures
· Olfactory sensitivity: Strong perfumes and cleaning products
· Spatial awareness: Crowded environments and physical proximity
Studies reveal that these sensitivities vary in intensity. Some people experience physical pain from everyday stimuli that others might not even notice [31].
Impact on Daily Function
Recent research shows that sensory processing difficulties disrupt both professional and personal life. Work performance often suffers because of decreased concentration in stimulating environments. Social interactions become harder when people need to manage multiple sensory inputs at once.
People often experience physical symptoms with sensory overload, like headaches, dizziness, and extreme fatigue. Some individuals show under-responsiveness and seek intense sensory experiences to stay focused and alert.
Environmental Adaptations
Managing sensory challenges requires an accommodating environment. Research supports several strategies that work :
Clear communication about needs with colleagues and family members helps build understanding.
Using noise-canceling headphones or earplugs can reduce auditory overwhelm.
A consistent daily routine helps reduce sensory stress.
Occupational therapy has shown positive results. On top of that, sensory integration therapy helps develop better processing strategies, especially when combined with environmental changes. Understanding these sensory patterns is vital for accurate ADHD diagnosis and effective treatment planning.

Image Source: Lilo Wellness
Research shows that 75% - 81% of individuals with ADHD have major working memory problems. These memory challenges are central to ADHD symptoms.
Types of Memory Affected
Working memory deficits are the biggest memory challenge for people with ADHD. They limit how well someone can hold and process information. Short-term memory, particularly tasks concerning visuospatial processing ability, might result in lower performance. Previously, scientists believed that ADHD had a direct impact on long-term memory but new studies suggest ADHD mainly affects how the brain encodes and stores information.
Real-life Impact
Memory problems show up in many daily challenges. People with working memory deficits find it hard to complete tasks and follow instructions. Majority of children with ADHD have trouble with working memory tasks. This affects their academic performance and organisational skills.
These memory difficulties often lead to:
· Forgetting household tasks and bill payments
· Struggling with multi-step instructions
· Misplacing essential items frequently
· Missing important deadlines and appointments
· Difficulty remembering conversations
Memory Support Strategies
Research shows certain strategies can help improve memory function. A well-laid-out approach helps manage these challenges better. Working memory training combined with positive feedback improves executive functions.
Physical activity helps manage ADHD symptoms and enhances brain function. Unlike what many believe, stimulant medications can improve brain areas linked to working memory. The best results often come from combining medication with behavioural strategies.
Simple memory support techniques work well. These include keeping consistent schedules, using visual reminders, and breaking complex information into smaller pieces. Good sleep plays a vital role in memory consolidation. Cognitive training exercises that focus on working memory can improve attention and problem-solving skills.

Image Source: Simply Psychology
Understanding memory patterns helps diagnose and treat ADHD accurately. Early recognition and treatment of memory challenges lets people develop effective coping strategies and support systems.

Image Source: Verywell Mind
ADHD masking affects about one-third of people with the condition and changes how they present themselves in social and professional settings. People use this coping mechanism to hide their ADHD symptoms and fit into neurotypical standards.
Understanding ADHD Masking
People develop masking behaviours early in life as they find ways to fit in with their peers. Research shows that girls and women tend to develop these compensatory behaviours more often. These behaviours demonstrate themselves as:
· Suppressing natural movements and fidgeting
· Creating complex systems to hide disorganisation
· Practicing social responses repeatedly
· Overcompensating through perfectionism
· Avoiding social situations to hide symptoms
Cost of Long-term Masking
Constant masking takes a heavy emotional toll. Studies reveal that long-term masking often results in anxiety and depression. People who involve themselves in masking also report high social anxiety and worry that others might see through their "performance".
These masks demand immense mental and emotional energy. The exhaustion shows up as burnout symptoms, including physical fatigue and damaged relationships. Research shows that masking can make proper ADHD diagnosis harder or impossible, especially for women who might develop advanced masking strategies early on.
Path to Authentic Living
Living authentically starts with understanding that ADHD masking, while protective at first, becomes harmful over time. Studies indicate that people who start unmasking feel "liberated" and "more effective" at work.
The trip to authentic living has several vital steps. You need to identify which masking behaviours help versus hurt, and develop self-compassion by understanding that ADHD traits aren't character flaws.
Professional support is a vital part of this change. Therapy helps break negative thought patterns and improves authentic self-expression. A supportive environment makes all the difference - research shows that people feel more comfortable being themselves around understanding colleagues and family members.
Unmasking might be challenging, but it often improves work performance and increases happiness. Only when we are willing to recognise and gradually release unnecessary masks can we focus our energy on developing real coping strategies and embracing our unique strengths.
Comparison Table
ADHD Sign | Prevalence/ Statistics | Key Manifestations | Effect on Daily Life | Management Strategies |
Chronic Time Blindness | About 57% struggle to avoid procrastination; 80% have time management issues | Poor sense of passing time; hard to estimate how long tasks take | Always running late; missing deadlines; rushed work | Digital tools; multiple alarms; body-doubling; visual timers |
Intense Emotional Reactions | 30-70% of adults show emotional regulation issues | Strong reactions; trouble calming down; gets frustrated easily | Strains relationships; overwhelming feelings that persist | Mindfulness practices; journaling; CBT; medication |
Hyperfocus | Not specified | Gets completely absorbed in tasks; loses track of time; struggles to switch tasks | Missed deadlines; skips meals; relationship strain | Timer use; calendar systems; accountability partners |
Decision Paralysis | Not specified | Struggles with everyday choices; mental overload; information processing issues | Lower motivation; higher stress; delayed tasks | Time limits; templates; smaller decisions; regular breaks |
Social Overwhelm | More than half face peer rejection | Trouble handling multiple social cues; mental fatigue; physical symptoms | Avoids social events; anxious about gatherings | "Reboot days"; setting boundaries; planned breaks |
Perfectionism | Most common thought pattern in ADHD adults | Start-to-finish perfectionism; harsh self-judgment | Avoids tasks; increased stress; gets less done | Smaller task goals; questioning negative thoughts |
Sensory Processing | Up to 60% affected | Reacts strongly or weakly to stimuli; can't filter input well | Lower work performance; physical discomfort | Changes to environment; noise-canceling gear; occupational therapy |
Memory Inconsistencies | 75-81% have working memory issues | Working memory problems; visual-spatial processing challenges | Forgets tasks; misses deadlines; loses items | Structured routines; visual reminders; memory exercises |
Masking Symptoms | About one-third of people | Hides natural behaviors; creates complex systems; practices social responses | Leads to anxiety; depression; burnout; late diagnosis | Professional help; therapy; supportive settings |
Conclusion
Recognising subtle ADHD signs is a vital step to understand and manage this complex condition. Each person's experience is different, and these nine indicators show how ADHD extends beyond traditional symptoms. Time blindness and masking behaviours create a detailed picture of the condition.
Research shows that adults often face these challenges quietly. Emotional dysregulation affects up to 70% of people, while perfectionism impacts 81% of cases. These traits are not personal failures - they are ADHD symptoms that need effective coping strategies.
When to Consider ADHD Diagnosis & Therapy
A professional diagnosis is necessary to get proper treatment. Being aware of these subtle signs can help you begin a journey toward diagnosis. Managing ADHD becomes easier when you understand your specific challenges like sensory processing difficulties, decision paralysis, or social overwhelm.
The way forward needs both acceptance and action. Knowledge about these overlooked signs helps you promote your needs and find appropriate support. This understanding can turn daily challenges into opportunities that stimulate growth and better self-management.
FAQs
Q1. What are some commonly overlooked signs of ADHD in adults? Some often-missed ADHD signs in adults include chronic time blindness, intense emotional reactions, hyperfocus on interesting tasks, decision paralysis, and social overwhelm. These subtle indicators can significantly impact daily functioning and relationships.
Q2. How does ADHD affect emotional regulation? ADHD can lead to emotional dysregulation, with 30% to 70% of adults experiencing difficulties managing their emotions. This can manifest as disproportionate reactions, trouble calming down, and low frustration tolerance, impacting personal and professional relationships.
Q3. What is ADHD masking and how does it affect individuals? ADHD masking involves deliberately hiding symptoms to conform to neurotypical standards. About one-third of individuals with ADHD engage in masking behaviors, which can lead to anxiety, depression, and burnout over time. It may also delay proper diagnosis, especially in women.
Q4. How does ADHD impact decision-making abilities? ADHD can cause decision paralysis due to executive function difficulties. Individuals may struggle with "cold decisions" requiring careful analysis, experience cognitive overload from multiple options, and face challenges in information processing, leading to decreased motivation and increased stress.
Q5. What strategies can help manage ADHD-related memory inconsistencies? To manage memory challenges associated with ADHD, individuals can implement structured schedules, use visual reminders, engage in working memory training, and break down complex information into smaller chunks. Additionally, maintaining consistent routines and getting adequate sleep can support memory function.
Redwood Psychology offers consultation and therapy services for people with ADHD. Contact us to consult with an experienced and qualified psychologist.

